集合
集合的框架体系


Collection
Collection 接口实现类的特点
public interface Collection
- collection 实现子类可以存放多个元素,每个元素可以是 Object
- 有些 Collection 的实现类,可以存放重复的元素,有些不可以
- Collection 的实现类,有些是有序的(List),有些不是有序的(Set)
- Collection 接口没有直接实现子类,是通过它的子接口 Set 和 List 来实现的
常用方法

package com.bbedu.collection_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class CollectionMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
// add
list.add("Tim");
list.add(10); // 相当于list.add(new Integer(10))
list.add(true);
System.out.println("list=" + list);
// remove
list.remove(0); // 删除第一个元素
list.remove((Integer) 10);
System.out.println("list=" + list);
// contains
System.out.println(list.contains(true));
// size
System.out.println(list.size());
// isEmpty
System.out.println(list.isEmpty());
// clear
list.clear();
System.out.println("list=" + list);
// addAll
ArrayList list2 = new ArrayList();
list2.add("红楼梦");
list2.add("三国演义");
list.addAll(list2);
System.out.println("list=" + list);
// containsAll
System.out.println(list.containsAll(list2));
// removeAll
list.add("Macbeth");
list.removeAll(list2);
System.out.println("list=" + list);
}
}迭代器遍历

Iterable 类中,可以返回一个 Iterator 对象,迭代器,可以用来遍历
- Iterator对象称为迭代器,主要用于遍历Collection集合中的元素。
- 所有实现了Collection接口的集合类都有一个iterator()方法,用以返回一个实现了lterator接口的对象,即可以返回一个迭代器。
lterator的结构:
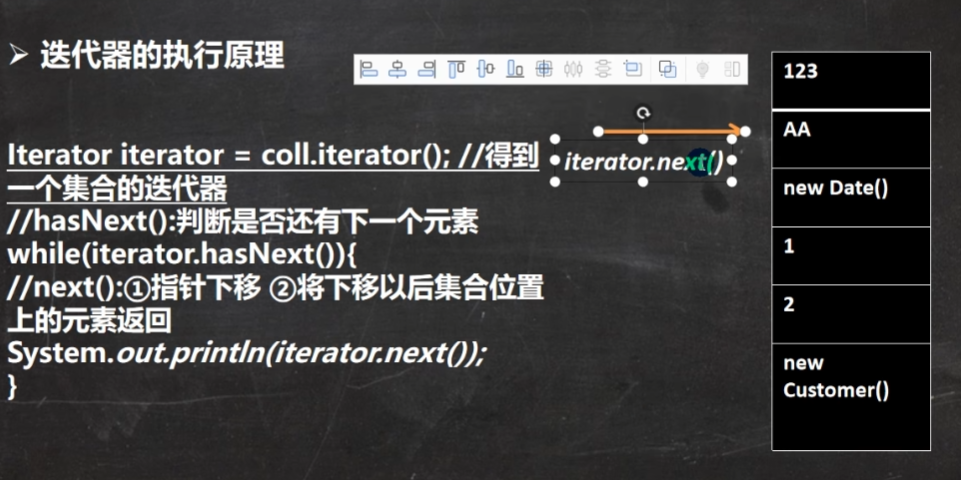
- Iterator仅用于遍历集合,Iterator本身并不存放对象。
增强 for 循环
增强 for 循环,可以替代 iterator 迭代器,特点:增强 for 就是简化版的 iterator,本质相同。但只能用于遍历集合和数组
基本语法:
for(元素类型 元素名 : 集合名或数组名){
访问元素;
}
练习

package com.bbedu.collection_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class CollectionExercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Dog> dogs = new ArrayList<>();
Dog dog1 = new Dog("小黑", 3);
Dog dog2 = new Dog("大黄", 5);
Dog dog3 = new Dog("旺财", 6);
dogs.add(dog1);
dogs.add(dog2);
dogs.add(dog3);
Iterator<Dog> iterator = dogs.iterator();
System.out.println("=====迭代器=====");
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Dog next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
System.out.println("=====增强for循环=====");
for (Dog dog : dogs) {
System.out.println(dog);
}
}
}
class Dog {
private String name;
private int age;
public Dog(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}List 接口
基本介绍
List 接口是 Collection 接口的子接口
- List集合类中元素有序(即添加顺序和取出顺序一致)、且可重复
- List集合中的每个元素都有其对应的顺序索引,即支持索引
- List容器中的元素都对应一个整数型的序号记载其在容器中的位置,可以根据序号存取容器中的元素
常用方法

package com.bbedu.list_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ListMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// add
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
list.add("计算机组成原理");
list.add("操作系统");
list.add(1, "数据结构"); // 插入指定位置
System.out.println("list=" + list);
// addAll
ArrayList list2= new ArrayList();
list2.add("Tim");
list2.add("Mike");
list.addAll(1, list2);
System.out.println("list=" + list);
// indexOf lastIndexOf
System.out.println(list.indexOf("Tim"));
list.add("Tim");
System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf("Tim"));
// remove
list.remove(0);
System.out.println("list=" + list);
// set 相当于替换
list.set(0, "Jim");
System.out.println("list=" + list);
// subList 范围:[fromIndex, toIndex)
List retList = list.subList(0, 2);
System.out.println("returnList=" + retList);
}
}List 的三种遍历
- iterator
- 增强 for
- 普通 for
练习
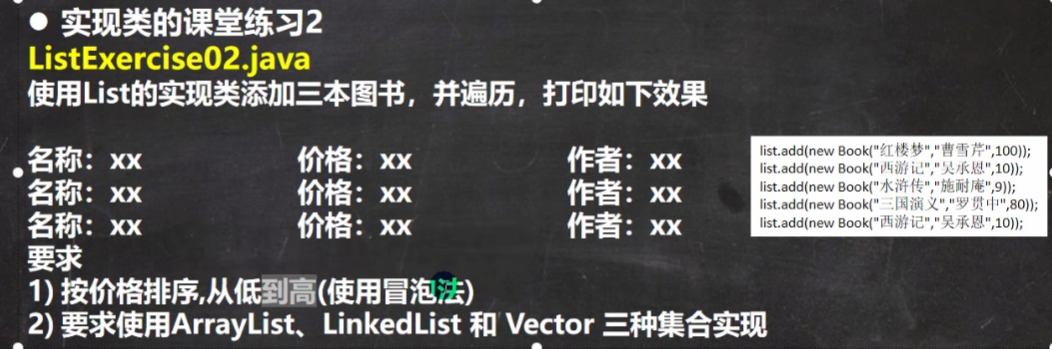
package com.bbedu.list_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Vector;
public class ListExercise02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
// List list = new LinkedList();
// List list = new Vector();
list.add(new Book("红楼梦", 100, "曹雪芹"));
list.add(new Book("西游记", 10, "吴承恩"));
list.add(new Book("水浒传", 19, "施耐庵"));
list.add(new Book("三国演义", 20, "罗贯中"));
list.add(new Book("西游记", 10, "吴承恩"));
for (Object o : list) {
System.out.println(o);
}
sort(list);
System.out.println("=====排序后=====");
for (Object o : list) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
public static void sort(List list){
for (int i = 0; i < list.size() - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < list.size() - i - 1; j++) {
Book book1 = (Book) list.get(j);
Book book2 = (Book) list.get(j + 1);
if(book1.getPrice() > book2.getPrice()){
list.set(j, book2);
list.set(j+1, book1);
}
}
}
}
}
class Book {
private String name;
private int price;
private String author;
public Book(String name, int price, String author) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
this.author = author;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "名称:" + name + "\t 价格:" + price + "\t 作者:" + author;
}
}ArrayList
注意事项
- permits all elements, including null
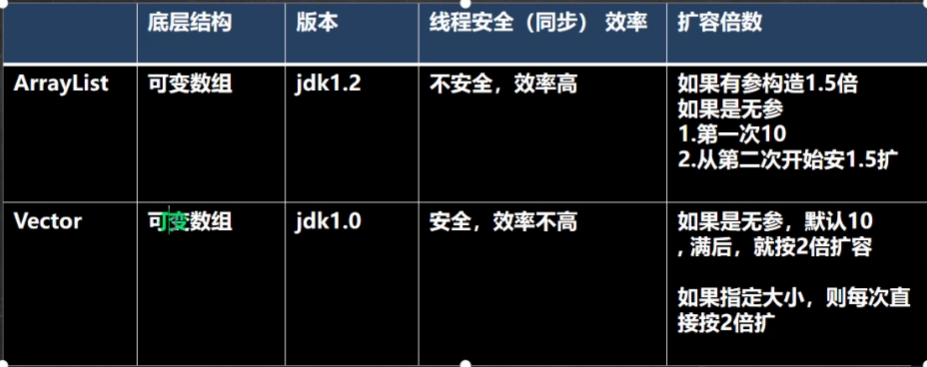
- ArrayList 是由数组来实现数据存储的
- ArrayList 基本等同于 Vector,除了 ArrayList 是线程不安全,在多线程情况下,不建议使用 ArrayList
底层结构和源码分析
先结论,再源码
- ArrayList中维护了一个Object类型的数组elementData. [debug 看源码]
transient Object[] elementData; //transient表示瞬间,短暂的,表示该属性不会被序列化 - 当创建ArrayList对象时,如果使用的是无参构造器,则初始elementData容量为0,第1次添加,则扩容elementData为10,如需要再次扩容,则扩容elementData为1.5倍。
- 如果使用的是指定大小的构造器,则初始elementData容量为指定大小,如果需要扩容,则直接扩容elementData为1.5倍。
package com.bbedu.list_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Vector;
public class ArrayListSource {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList(8);
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
for (int i = 11; i <= 15; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
list.add(100);
list.add(200);
list.add(300);
}
}


初始为10:


若先指定 ArrayList 大小,底层类似,不再赘述
Vector
注意事项
Vector 类的定义说明

- Vector 底层也是一个对象数组,
protected Object[] elementData; - Vector 是线程同步的,即线程安全,Vector 类的操作方法带有 synchronized
- 在开发中,需要线程同步安全时,考虑使用 Vector
Vector 和 ArrayList 比较
扩容源码分析
package com.bbedu.list_;
import java.util.Vector;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class Vector_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector vector = new Vector();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
vector.add(i);
}
vector.add(100);
}
}

LinkedList
- LinkedList 底层实现了双向链表和双向队列特点
- 可以添加任意元素(元素可以重复),包括 null
- 线程不安全,没有实现同步
LinkedList 的底层操作机制
- LinkedList 底层维护了一个双向链表
- LinkedList 中维护了两个属性 first 和 last 分别指向 首节点和尾节点
- 每个节点(Node对象)里又维护了 prev、next、item 三个属性,其中通过 prev 指向前一个,通过 next 指向后一个节点,最终实现双向链表
- LinkedList 的元素的添加和删除,不是通过数组完成的,因此效率相对较高
package com.bbedu.list_;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class LinkedListCRUD {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.add(1);
linkedList.add(2);
linkedList.add(3);
System.out.println("linkedList=" + linkedList);
linkedList.remove(); // 默认删除第一个节点
System.out.println("linkedList=" + linkedList);
linkedList.set(0, 999);
System.out.println("linkedList=" + linkedList);
linkedList.get(1);
System.out.println(linkedList.get(1));
Iterator iterator = linkedList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println("next=" + next);
}
for (Object o : linkedList) {
System.out.println("o=" + o);
}
}
}jdk底层研究方法类似,请自行研究。
ArrayList 和 LinkedList 比较

如何选择ArrayList和LinkedList:
- 如果我们改查的操作多,选择ArrayList
- 如果我们增删的操作多,选择LinkedList
- 一般来说,在程序中,80%-90%都是查询,因此大部分情况下会选择ArrayList
- 在一个项目中,根据业务灵活选择,也可能这样,一个模块使用的是ArrayList, 另外一个模块是 LinkedList.
Set 接口
基本介绍
- 无序(添加和取出的顺序不一致),没有索引
- 不允许重复元素,所以最多包含一个null
- JDK API 中 Set 接口的实现类有:

常用方法
和 List 接口一样,Set 接口也是 Collection 的子接口,因此常用方法和 Collection 接口一样
遍历方法
同 Collection 的遍历方式一样,因为 Set 接口是 Collection 接口的子接口:
- 可以使用迭代器
- 增强 for 循环
- 不能使用 索引的方式来获取
package com.bbedu.set_;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class SetMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set = new HashSet();
set.add("john");
set.add("lucy");
set.add("john");
set.add("job");
set.add(null);
System.out.println("set=" + set);
System.out.println("====迭代器====");
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println("next=" + next);
}
set.remove(null);
System.out.println("====增强for====");
for (Object o : set) {
System.out.println("o=" + o);
}
}
}HashSet
- HashSet 实现了 Set 接口
- HashSet 底层实际上是是 HashMap
- 不能有重复的元素,可以存放 null,但是只能有一个 null
- HashSet 不保证元素是有序的,取决于 Hash 后,再确定索引的结果
package com.bbedu.set_;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class HashSet01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
System.out.println(hashSet.add("John"));
System.out.println(hashSet.add("Lucy"));
System.out.println(hashSet.add("John"));
System.out.println(hashSet.add("Jack"));
System.out.println(hashSet.add("Tim"));
// 指定删除对象
hashSet.remove("John");
System.out.println("set=" + hashSet);
hashSet = new HashSet();
System.out.println("set=" + hashSet);
hashSet.add("lucy");
hashSet.add("lucy");
hashSet.add(new Dog("coco")); // OK
hashSet.add(new Dog("coco")); // OK
System.out.println("set=" + hashSet);
// 看源码理解
// 不能添加重复元素的真正含义?
hashSet.add(new String("bbchen")); // ok
hashSet.add(new String("bbchen")); // no
System.out.println("set=" + hashSet);
}
}
class Dog {
private String name;
public Dog(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}HashSet 底层机制说明
分析 HashSet 底层是 HashMap, HashMap 底层是(数组 + 链表 + 红黑树)
数组+链表=邻接表,理解邻接表:
package com.bbedu.set_;
/**
* 模拟邻接表
*/
public class HashSetStructure {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Node[] 数组 称为 表
Node[] table = new Node[16];
Node john = new Node("john", null);
table[2] = john;
Node jack = new Node("jack", null);
john.next = jack;
Node rose = new Node("Rose", null);
jack.next = rose;
}
}
class Node {
Object item;
Node next;
public Node(Object item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}分析 HashSet 的添加元素底层是如何实现的
同样,先结论,后Debug

源码分析:
初始化HashSet()
/** * Constructs a new, empty set; the backing {@code HashMap} instance has * default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75). */ public HashSet() { map = new HashMap<>(); }add()
/** * Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present. * More formally, adds the specified element {@code e} to this set if * this set contains no element {@code e2} such that * {@code Objects.equals(e, e2)}. * If this set already contains the element, the call leaves the set * unchanged and returns {@code false}. * * @param e element to be added to this set * @return {@code true} if this set did not already contain the specified * element */ public boolean add(E e) { return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null; }put(),先执行 hash(key),得到对应的 hash 值,并不直接是 hashCode()
/** * Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map. * If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old * value is replaced. * * @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated * @param value value to be associated with the specified key * @return the previous value associated with {@code key}, or * {@code null} if there was no mapping for {@code key}. * (A {@code null} return can also indicate that the map * previously associated {@code null} with {@code key}.) */ public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); }hash()
/** * Computes key.hashCode() and spreads (XORs) higher bits of hash * to lower. Because the table uses power-of-two masking, sets of * hashes that vary only in bits above the current mask will * always collide. (Among known examples are sets of Float keys * holding consecutive whole numbers in small tables.) So we * apply a transform that spreads the impact of higher bits * downward. There is a tradeoff between speed, utility, and * quality of bit-spreading. Because many common sets of hashes * are already reasonably distributed (so don't benefit from * spreading), and because we use trees to handle large sets of * collisions in bins, we just XOR some shifted bits in the * cheapest possible way to reduce systematic lossage, as well as * to incorporate impact of the highest bits that would otherwise * never be used in index calculations because of table bounds. */ static final int hash(Object key) { int h; return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); }*putVal,核心代码!!!
/** * Implements Map.put and related methods. * * @param hash hash for key * @param key the key * @param value the value to put * @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value * @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode. * @return previous value, or null if none */ final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length; if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else { Node<K,V> e; K k; if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p; else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); else { for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; }
练习

package com.bbedu.set_;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Objects;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class HashSetExercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add(new Employee("Jack", 20));
hashSet.add(new Employee("Mary", 18));
hashSet.add(new Employee("Jack", 20));
Iterator iterator = hashSet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println("next=" + next);
}
}
}
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
class Employee {
private String name;
private int age;
public Employee(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Employee employee = (Employee) o;
return age == employee.age && Objects.equals(name, employee.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
package com.bbedu.set_;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Objects;
public class HashSetExercise02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
hashSet.add(new Employee02("Tim", 20000, new MyDate(1990, 1, 1)));
hashSet.add(new Employee02("Rock", 15000, new MyDate(1998, 4, 29)));
hashSet.add(new Employee02("Tim", 23333, new MyDate(1990, 1, 1)));
Iterator iterator = hashSet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println("next=" + next);
}
}
}
class Employee02{
private String name;
private double sal;
private MyDate birthday;
public Employee02(String name, double sal, MyDate birthday) {
this.name = name;
this.sal = sal;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSal() {
return sal;
}
public void setSal(double sal) {
this.sal = sal;
}
public MyDate getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(MyDate birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Employee02 that = (Employee02) o;
return Objects.equals(name, that.name) && Objects.equals(birthday, that.birthday);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, birthday);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee02{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", sal=" + sal +
", birthday=" + birthday +
'}';
}
}
class MyDate {
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
public MyDate(int year, int month, int day) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month = month;
}
public int getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(int day) {
this.day = day;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
MyDate myDate = (MyDate) o;
return year == myDate.year && month == myDate.month && day == myDate.day;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(year, month, day);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyDate{" +
"year=" + year +
", month=" + month +
", day=" + day +
'}';
}
}LinkedHashSet

- LinkedHashSet 是 HashSet 的子类
- LinkedHashSet 底层是一个 LinkedHashMap,底层维护了一个 数组 + 双向链表
- LiniedHashSet 根据元素的 hashCode 值来决定元素的存储位置,同时使用链表维护元素的次序,这使得元素看起来是以插入顺序保存的
- LinkedHashSet 不允许添加重复元素

Map 接口
- Map 与 Collection 并列存在,用于保存具有映射关系的数据:Key-Value (双列元素)
- Map 中的 key 和 value 可以是任何引用类型的数据,会封装到 HashMap$Node 对象中
- Map 中的 key不允许重复,当有相同的 key 时,相当于替换
- Map 中的 value 可以重复
- key 和 value 都可以为 null,但 key 只能有一个 null,而 value 可以有多个 null
- 常用 String 类来做 key,别的引用类型同样可以
- key 和 value 存在单向一对一关系(满射关系,即一种映射)
常用方法
六种遍历方法:
package com.bbedu.map_;
import java.util.*;
public class MapFor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put("刘慈欣", "三体");
hashMap.put("张爱玲", "倾城之恋");
hashMap.put("萧红", "呼兰河传");
hashMap.put("托尔斯泰", "复活");
hashMap.put("史铁生", "我与地坛");
// 第一组
Set set = hashMap.keySet();
System.out.println("===增强for===");
for (Object o : set) {
System.out.println(o + "-" + hashMap.get(o));
}
System.out.println("===迭代器===");
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next + "-" + hashMap.get(next));
}
// 第二组
Collection values = hashMap.values();
System.out.println("===取value===");
for (Object value : values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
System.out.println("===迭代器===");
Iterator iterator1 = values.iterator();
while (iterator1.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator1.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
// 第三组
Set set1 = hashMap.entrySet();
System.out.println("===增强for===");
for (Object o : set1) {
Map.Entry o1 = (Map.Entry) o;
System.out.println(o1.getKey() + "-" + o1.getValue());
}
System.out.println("===迭代器===");
Iterator iterator2 = set1.iterator();
while (iterator2.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator2.next();
Map.Entry next1 = (Map.Entry) next;
System.out.println(next1.getKey() + "-" + next1.getValue());
}
}
}
练习

package com.bbedu.map_;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class MapExercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer,Employee> map = new HashMap();
Employee tom = new Employee("Tom", 20000, 1);
Employee bob = new Employee("Bob", 15000, 2);
Employee sam = new Employee("Sam", 19000, 3);
map.put(tom.getId(), tom);
map.put(bob.getId(), bob);
map.put(sam.getId(), sam);
System.out.println("===方式1===");
Set set = map.keySet();
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator.next();
Employee employee = (Employee) map.get(next);
if(employee.getSal() > 18000){
System.out.println(employee);
}
}
System.out.println("===方式2===");
Set set1 = map.entrySet();
for (Object o : set1) {
Map.Entry o1 = (Map.Entry) o;
Employee value = (Employee) o1.getValue();
if(value.getSal() > 18000){
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}
}
class Employee {
private String name;
private double sal;
private int id;
public Employee(String name, double sal, int id) {
this.name = name;
this.sal = sal;
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSal() {
return sal;
}
public void setSal(double sal) {
this.sal = sal;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", sal=" + sal +
", id=" + id +
'}';
}
}HashMap
底层机制及源码分析
先结论:


Hashtable
- 存放的元素是键值对,即 K-V
- Hashtable 的键和值都不能为null,否则会抛出 NullPointerException
- Hashtable 使用的方法基本上和 HashMap一样
- Hashtable 是线程安全的,HashMap 是线程不安全的
扩容机制


Hashtable 和 HashMap 对比

Properties
- Properties 类继承自 Hashtable 类并且实现了 Map 接口,也是使用一种键值对的形式来保存数据
- 它的特点和 Hashtable 类似
- Properties 还可以用于 从 xxx.properties 文件中加载数据到Properties 类对象,并进行读取和修改
开发中如何选择集合实现类

TreeSet

TreeMap
TreeMap 是 TreeSet 的底层
Collections 工具类
常用方法
package com.bbedu.collections_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Collections_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ArrayList 集合,用于测试
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
list.add("tom");
list.add("jack");
list.add("sam");
list.add("mike");
list.add("smith");
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println("===reverse===");
Collections.reverse(list);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println("===shuffle===");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Collections.shuffle(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
System.out.println("===sort====");
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println("===自定义sort===");
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<>() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
if(o1 instanceof String && o2 instanceof String){
return ((String) o1).length() - ((String) o2).length();
}
return 0;
}
});
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println("===swap===");
Collections.swap(list,0, 1);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println("===max===");
System.out.println(Collections.max(list));
System.out.println("===自定义max===");
Object max = Collections.max(list, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return ((String) o1).length() - ((String) o2).length();
}
});
System.out.println(max);
System.out.println("===frequency===");
System.out.println(Collections.frequency(list, "tom"));
System.out.println("===copy===");
ArrayList dest = new ArrayList();
// 需要先给 dest 赋值,大小和 list相同
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
dest.add("");
}
Collections.copy(dest, list);
System.out.println(dest);
System.out.println("===replaceAll===");
Collections.replaceAll(list, "tom", "汤姆");
System.out.println(list);
}
}本章作业

package com.bbedu.homework;
import java.util.ArrayList;
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public class Homework01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
arrayList.add(new News("广东中山发现8例无症状感染者,均在隔离管控的密接人员中发现"));
arrayList.add(new News("经济衰退阴云笼罩 惠誉下调美国2023年GDP增速预期"));
for (int i = arrayList.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
News news = (News) arrayList.get(i);
String s = processTitle(news.getTitle());
System.out.println(s);
}
}
public static String processTitle(String title) {
if (title == null) {
return "";
}
if (title.length() > 15){
return title.substring(0, 15) + "...";
}else{
return title;
}
}
}
class News {
private String title;
private String content;
public News(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "News{" +
"title='" + title + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.bbedu.homework;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Homework02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car car1 = new Car("宝马", 300000);
Car car2 = new Car("奔驰", 400000);
Car car3 = new Car("宾利", 500000);
ArrayList<Car> cars = new ArrayList<>();
cars.add(car1);
cars.add(car2);
cars.add(car3);
System.out.println(cars);
System.out.println("===增强for===");
for (Car car : cars) {
System.out.println(car);
}
cars.remove(car3);
System.out.println(cars);
System.out.println(cars.contains(car3));
System.out.println(cars.isEmpty());
cars.clear();
System.out.println(cars);
cars.add(car1);
cars.add(car2);
cars.add(car3);
ArrayList<Car> cars1 = new ArrayList<>();
cars1.addAll(cars);
System.out.println(cars1);
System.out.println(cars1.containsAll(cars));
cars1.removeAll(cars);
System.out.println(cars1);
}
}
class Car {
private String name;
private double price;
public Car(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
package com.bbedu.homework;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Set;
public class Homework03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
hashMap.put("jack", 650);
hashMap.put("tom", 1200);
hashMap.put("smith", 2900);
printAll(hashMap);
System.out.println("===修改jack工资===");
hashMap.replace("jack", 2600);
printAll(hashMap);
System.out.println("===所有人工资+100===");
Set set = hashMap.keySet();
for (Object o : set) {
hashMap.put(o, (Integer) hashMap.get(o) + 100);
}
printAll(hashMap);
}
public static void printAll(HashMap hashMap){
Set set = hashMap.keySet();
for (Object o : set) {
System.out.println(o + "-" + hashMap.get(o));
}
}
public static void printAllSal(HashMap hashMap){
Set set = hashMap.keySet();
for (Object o : set) {
System.out.println(hashMap.get(o));
}
}
}


package com.bbedu.homework;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class Homework05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet();
treeSet.add(new Person());
treeSet.add(new Person());
treeSet.add(new Person());
treeSet.add(new Person());
treeSet.add(new Person());
treeSet.add(new Person());
System.out.println(treeSet);
}
}
class Person implements Comparable{
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
return 0;
}
}
输出
[Person2{id=1002, name='BB'}, Person2{id=1001, name='CC'}]
[Person2{id=1002, name='BB'}, Person2{id=1001, name='CC'}, Person2{id=1001, name='CC'}]
[Person2{id=1002, name='BB'}, Person2{id=1001, name='CC'}, Person2{id=1001, name='CC'}, Person2{id=1001, name='AA'}]

评论