常用类
本章内容

包装类 Wrapper
- 针对八种基本数据类型相应的引用类型——包装类
- 有了类的特点,就可以调用类中的方法
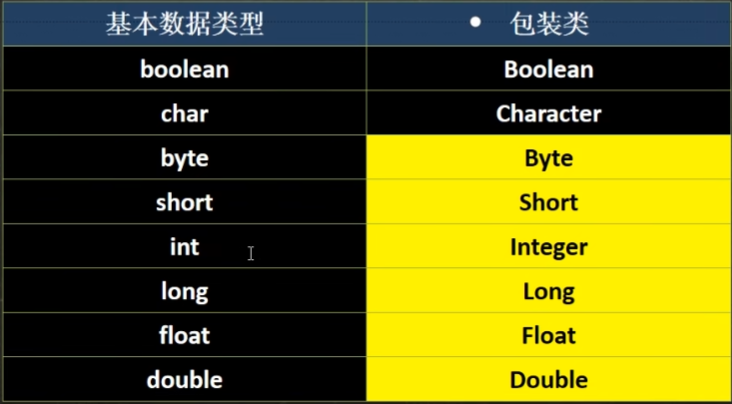
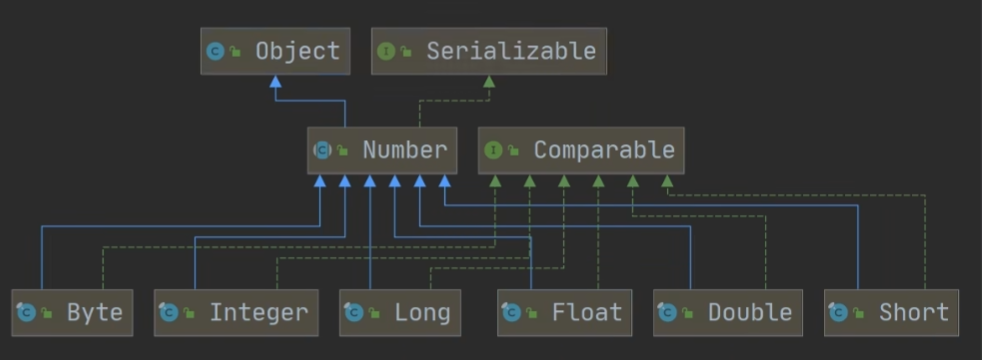


包装类和基本数据类型的转换
- jdk5 前的手动装箱和拆箱方式,装箱:基本类型 -> 包装类型,反正为拆箱
- jdk5 以后(含 jdk5)的自动装箱和拆箱方式
- 自动装箱底层调用的是 valueOf 方法,比如 Integer.valueOf()
package com.bbedu.wrapper;
public class Integer01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 演示 in Integer 的装箱和拆箱
// jdk5 之前手动
int n1 = 100;
Integer integer = new Integer(n1);
Integer integer1 = Integer.valueOf(n1);
int i = integer.intValue();
// jdk5 后自动装箱拆箱
int n2 = 500;
Integer integer2 = n2; // 底层是Integer.valueOf(n2)
int n3 = integer2; // 底层是intValue()方法
Object obj1 = true ? new Integer(1) : new Double(2.0);
System.out.println(obj1);
}
}
包装类和 String 类的转换
package com.bbedu.wrapper;
public class WrapperVSString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i = 100;
// Integer -> String
// 方式1
String str1 = i + "";
// 方式2
String str2 = i.toString();
// 方式3
String str3 = String.valueOf(i);
// String -> Integer
String str4 = "12345";
// 方式1
Integer i2 = Integer.parseInt(str4); // 使用到自动装箱
// 方式2
Integer i3 = new Integer(str4); // 构造器
}
}包装类的常用方法

很多,使用时查阅即可
Integer 细节

false
true
false
此处关键词:IntegerCache

String 类
- String 对象用于保存字符串,也就是一组字符序列
- 字符串常量对象是用双引号括起的字符序列,例如:"你好","Hello",”5.21”等
- 字符串的字符使用Unicode字符编码,一个字符占两个字节
String 类有很多构造器,构造器重载:
常用的有:
String s2 = new String(String original);
String s3 = new String(char[] a);
String s4 = new String(char[] a,int startIndex,int count);String s5 = new String(byte[] b);
String 类实现了 Serializable 接口,可以串行化,可以在网络传输
实现了 Comparable 接口,可以相互比较大小
- String 是 final 类,不能被继承
- String 有一个 private final char value[]; 用于存放字符串内容,一定要注意,value 是一个 final 类型,不可修改(即 value 不能指向新的地址,但是单个字符的内容可以变化)
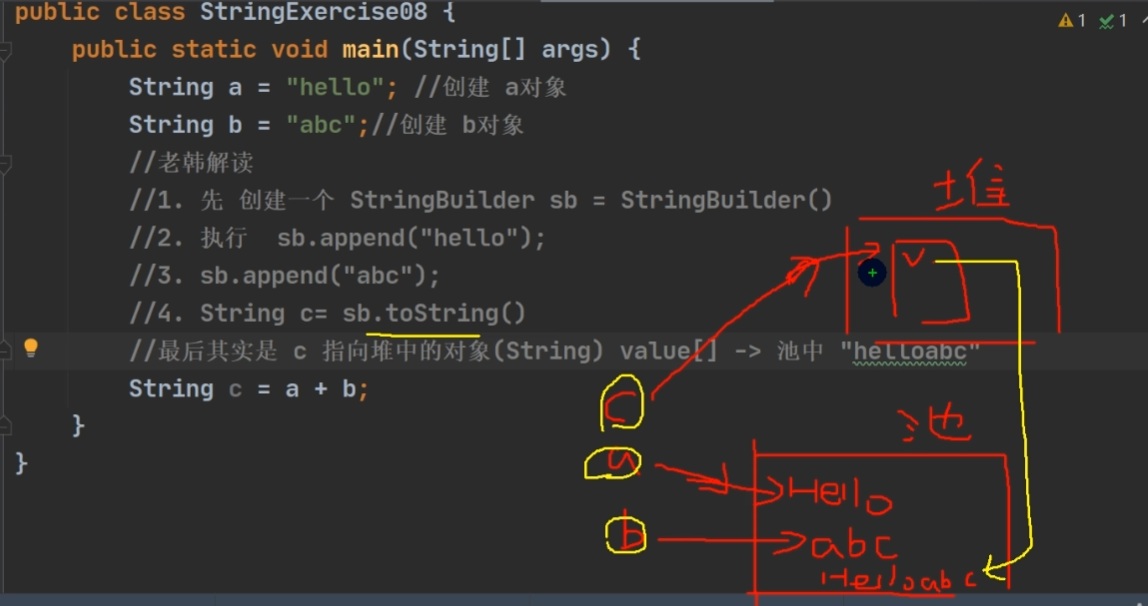
创建 String 对象的两种方式
方式一:直接赋值: String s = "bbedu"
方式二:调用构造器:String s = new String("bbedu");
区别
方式一:先从常量池查看是否有"bbedu"数据空间,如果有,直接指向;如果没有则重新创建,然后指向。s 最终指向的是常量池的空间地址
方式二:先在堆中创建空间,里面维护了 value 属性,指向常量池的bbedu空间,如果常量池没有"bbedu",重新创建,如果有直接通过 value 指向,最终指向的是堆中的空间地址

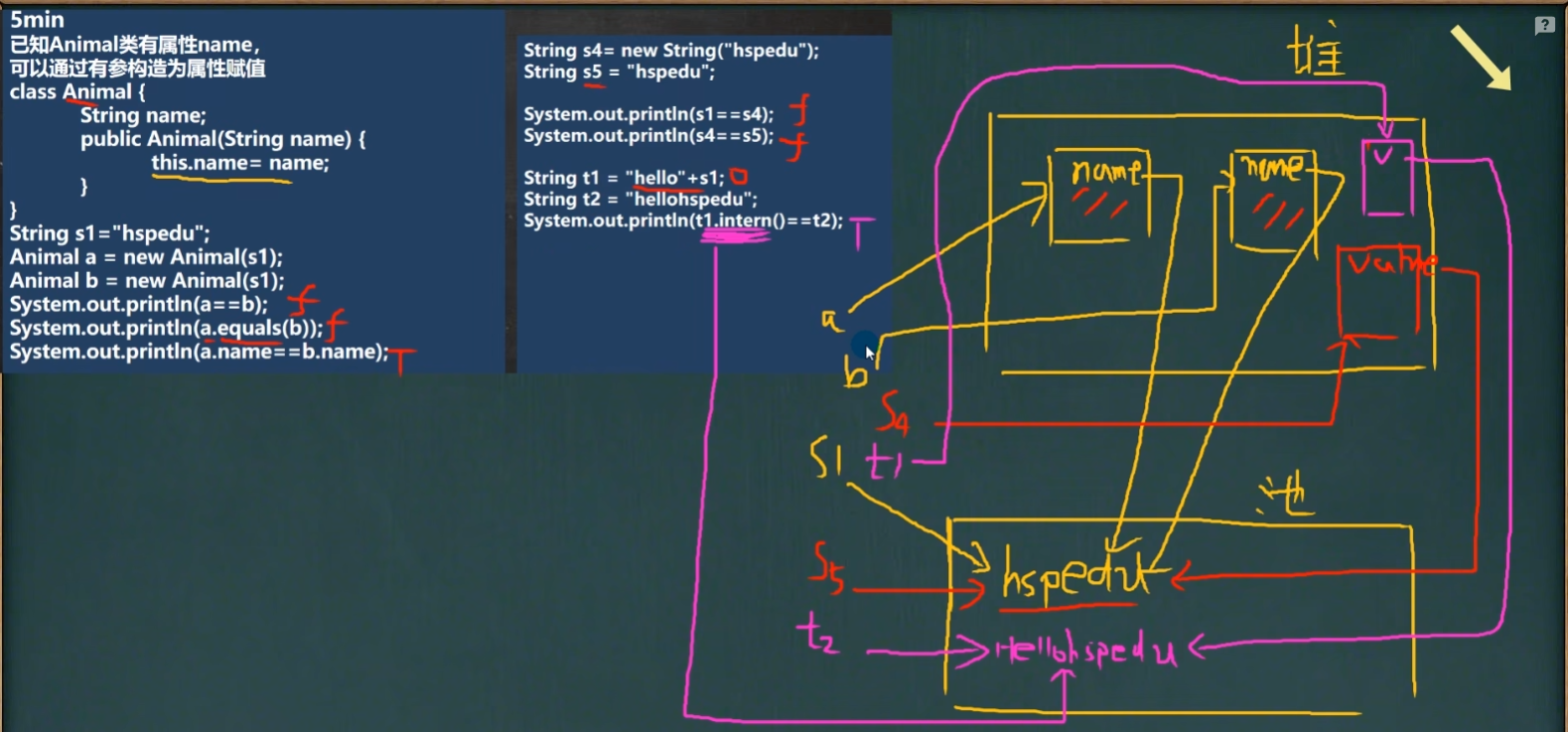
练习


T F T F
b.intern() 方法最终返回的是常量池的地址

F T T F

T T T F
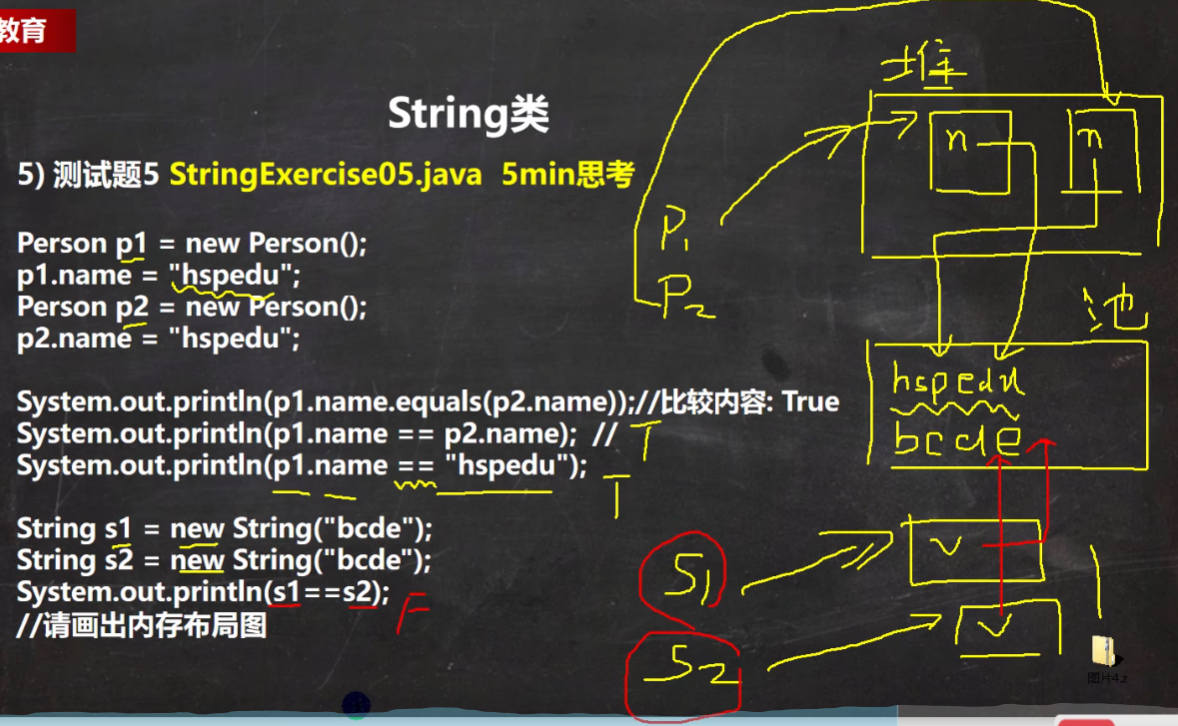



三个对象:如图所示


T T

输出:
hsp and hava

String 类的常用方法
String 类是保存字符串常量的,每次更新都需要重新开辟空间,效率较低,因此 java 设计者还提供了 StringBuilder 和 StringBuffer 来增强 String 的功能,并提高效率。

package com.bbedu.string_;
public class StringMethod01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.equals
String str1 = "hello";
String str2 = "Hello";
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2)); // false
// 2. equalsIgnoreCase
String username = "John";
if("john".equalsIgnoreCase(username)){
System.out.println("Success");
}else {
System.out.println("Failure");
}
// 3.length
System.out.println("bbchen".length());
// 4.indexOf
String s1 = "we@th@er";
System.out.println(s1.indexOf('@'));
System.out.println(s1.indexOf("we"));
System.out.println(s1.indexOf('#'));
// 5.lastIndexOf
System.out.println(s1.lastIndexOf('@'));
System.out.println(s1.lastIndexOf('#'));
// 6.substring
String name = "hello,world";
System.out.println(name.substring(6));
System.out.println(name.substring(0, 5));
}
}
package com.bbedu.string_;
public class StringMethod02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.toUpperCase
String s = "hello";
System.out.println(s.toUpperCase());
// 2.toLowerCase
System.out.println(s.toLowerCase());
// 3.concat
String s1 = ",world";
System.out.println(s.concat(s1));
// 4.replace
String str = "bb want to be Java developer";
System.out.println(str.replace("Java", "Python"));
System.out.println(str);
// 5.split
String poem = "锄禾日当午,汗滴禾下土";
String[] split = poem.split(",");
for (String value : split) {
System.out.println(value);
}
// 6.toCharArray
String s2 = "happy";
char[] chs = s2.toCharArray();
for (char ch : chs) {
System.out.println(ch);
}
// 7.compareTo
String a = "jr";
String b = "jack";
System.out.println(a.compareTo(b));
System.out.println('r' - 'a');
// 8.format
String name = "john";
String age = "10";
double score = 84.5 / 3;
char gender = '男';
String formatStr = "我的名字是%s, 今年%d岁, 得分为%.2f, 性别为%c";
String info = String.format(formatStr, name, Integer.parseInt(age), score, gender);
System.out.println(info);
}
}StringBuffer 类
java.lang.StringBuffer 代表可变的字符序列,可以对字符串内容进行增删
很多方法和 String 相同,但 StringBuffer 是可变长度的
StringBuffer 是一个容器
String vs StringBuffer
- String 保存的是字符串常量,里面的值不能更改,每次 String 类的更新实际上就是更改地址,效率较低 //private final byte[] value;
- StringBuffer 保存的是字符串变量,里面的值可以更改,每次StringBuffer 的更新实际上可以更新内容,不用每次更新地址,效率较高 //byte[] value;
String 和 StringBuffer 互相转换
package com.bbedu.stringbuffer_;
public class StringBuffer01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello tim";
// String -> StringBuffer
// 方式1
StringBuffer stringBuffer1 = new StringBuffer(str);
// 方式2
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer("hello");
stringBuffer = stringBuffer.append(str);
// StringBuffer -> String
StringBuffer bbchen = new StringBuffer("bbchen");
// 方式1.toString
String s = bbchen.toString();
// 方式2.构造器
String s1 = new String(bbchen);
}
}常见方法

package com.bbedu.stringbuffer_;
public class StingBufferMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer hello = new StringBuffer("hello");
// 1.append
hello.append(',');
hello.append("world");
System.out.println(hello);
// 2.delete
hello.delete(2, 4); // 删除下标[2,4)的字符
System.out.println(hello);
// 3.replace
hello.replace(4, 9, "bbchen");
System.out.println(hello);
// 4.indexOf
int index = hello.indexOf("e");
System.out.println(index);
// 5.insert
hello.insert(10, "gogogo");
System.out.println(hello);
// 6.length
System.out.println(hello.length());
}
}StringBuilder 类
- StringBuilder 继承 AbstractStringBuilder 类
- 实现了 Serializable,说明 StringBuilder 对象是可以串行化
- StringBuilder 是 final 类,不能被继承
- StringBuilder 对象字符序列仍然是存放在其父类 AbstractStringBuilder 的 byte[] value,因此字符序列是在堆中
- StringBuilder 的方法,没有做互斥的处理,即没有 synchronized 关键字,因此在单线程的情况下使用 StringBuilder
String, StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 的比较
- StringBuilder 和 StriBuffer 非常相似,均代表可变的字符序列,而且方法也一样
- String: 不可变字符序列,效率低,但是复用率高
- StringBuffer: 可变字符序列、效率较高、线程安全
- StringBuilder: 可变字符序列、效率最高、线程不安全
- String 使用说明:如果我们对 String 做大量修改,不要使用 String
结论
- 如果字符串存在大量的修改操作,一般使用StringBuffer 或StringBuilder
- 如果字符串存在大量的修改操作,并在单线程的情况,使用 StringBuilder
- 如果字符串存在大量的修改操作,并在多线程的情况,使用 StringBuffer
如果我们字符串很少修改,被多个对象引用,使用String, 比如配置信息等
StringBuilder的方法使用和 StringBuffer一样,不再赘述
Math 类

package com.bbedu.math_;
import java.io.FilterOutputStream;
public class MathMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 5.round
long round = Math.round(5.51);
System.out.println(round);
// 6.sqrt
double sqrt = Math.sqrt(9);
System.out.println(sqrt);
// 7.random 返回 [0, 1) 直接的随机小数
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//返回 [2, 7] 的随机整数
System.out.println((int)(Math.random() * 6 + 2));
}
// max, min
int min = Math.min(1, 9);
int max = Math.max(4, 20);
System.out.println(min);
System.out.println(max);
}
}Arrays 类
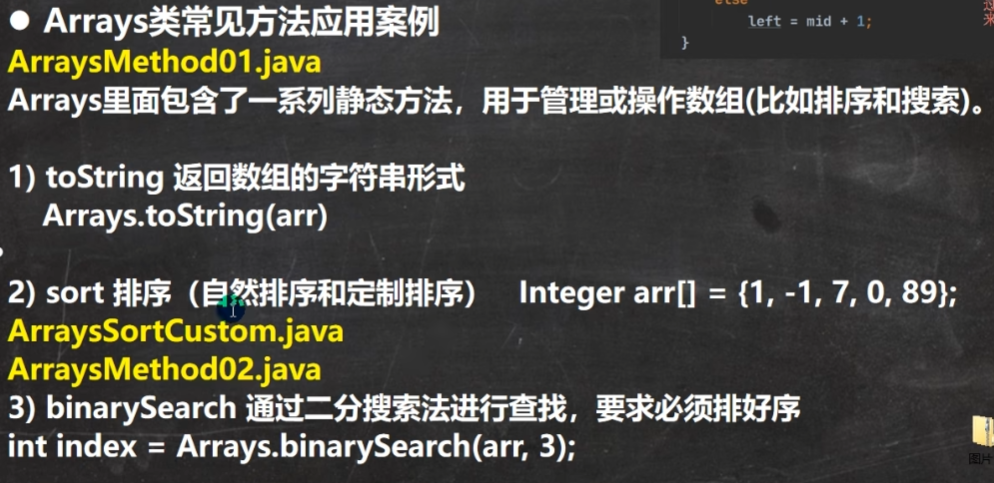
Comparator原理:
while (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) >>> 1;
if (c.compare(pivot, a[mid]) < 0)
right = mid;
else
left = mid + 1;
}package com.bbedu.arrays_;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class ArrayMethod01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// toString
Integer[] integers = {1, 20, 90};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(integers));
// sort
Integer[] arr = {1, -1, 31, 3, 2, 53, 9, 20};
Arrays.sort(arr); // 默认排序方法
// 定制排序, 体现接口编程的方式
Arrays.sort(arr, new Comparator<Integer>() {
// 匿名内部类
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
});
System.out.println("Sorted:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}package com.bbedu.arrays_;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class ArraysSortCustom {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {0, -3, 20, 14, 23, 43, 21};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
bubble02(arr, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
int i1 = (Integer) o1;
int i2 = (Integer) o2;
return i2 - i1;
}
});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
// 使用冒泡排序
public static void bubble01(int[] arr){
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - i - 1; j++) {
if(arr[j] > arr[j + 1]){
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
// 结合冒泡 + 定制
public static void bubble02(int[] arr, Comparator c){
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - i - 1; j++) {
// c
if(c.compare(arr[j], arr[j + 1]) > 0){
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}package com.bbedu.arrays_;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class ArraysMethod02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] arr = {1, 3, 5, 23, 100, 854, 1145};
// 二分查找,要求数组有序
// 不存在返回 return -(low + 1); // key not found.
int index = Arrays.binarySearch(arr, -23);
System.out.println(index);
// copyOf
// 拷贝长度 > arr.length ,在数组后加 null
Integer[] newArr = Arrays.copyOf(arr, arr.length + 1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(newArr));
// fill 数组填充
Integer[] num = new Integer[]{9, 3, 2};
Arrays.fill(num, 99);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num));
// equals 比较两数组是否完全一样,区分顺序
Integer[] arr2 = {3, 1, 5, 23, 100, 854, 1145};
boolean equals = Arrays.equals(arr, arr2);
System.out.println(equals);
// asList
List<Integer> integers = Arrays.asList(2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 1);
System.out.println(integers);
System.out.println(integers.getClass());
}
}练习

package com.bbedu.arrays_;
import java.util.Comparator;
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class ArraysExercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book[] books = new Book[4];
books[0] = new Book("红楼梦", 100);
books[1] = new Book("金瓶梅", 90);
books[2] = new Book("三体", 60);
books[3] = new Book("毛泽东选集", 300);
for (int i = 0; i < books.length; i++) {
System.out.println(books[i].toString());
}
// 按价格
// Book.sort(books, new Comparator() {
// @Override
// public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
// Book i1 = (Book) o1;
// Book i2 = (Book) o2;
//
// // 返回类型不一致,进行转换
// double priceVal = i2.getPrice() - i1.getPrice();
// if(priceVal > 0) {
// return -1;
// } else if (priceVal < 0) {
// return 1;
// }else {
// return 0;
// }
// }
// });
// 按照书名从长到短
Book.sort(books, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
Book i1 = (Book) o1;
Book i2 = (Book) o2;
return i1.getName().length() - i2.getName().length();
}
});
System.out.println("====排序后====");
for (int i = 0; i < books.length; i++) {
System.out.println(books[i].toString());
}
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("all")
class Book {
private String name;
private double price;
public Book(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
public static void sort(Book[] b, Comparator c){
Book book = null;
for (int i = 0; i < b.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < b.length - i - 1; j++) {
// 定义接口, 根据价格排序
if(c.compare(b[j], b[j + 1]) < 0){
book = b[j];
b[j] = b[j + 1];
b[j + 1] = book;
}
}
}
}
}System 类

package com.bbedu.system_;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class System_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// // exit 0为正常状态
// System.out.println("ok1");
// System.exit(0);
// System.out.println("ok2");
// arraycopy
// * @param src the source array.
// * @param srcPos starting position in the source array.
// * @param dest the destination array.
// * @param destPos starting position in the destination data.
// * @param length the number of array elements to be copied.
int[] arr1 = {1, 2, 3};
int[] arr2 = new int[3];
System.arraycopy(arr1, 0, arr2, 1, 2);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}BigInteger 和 BigDecimal 类

package com.bbedu.bignum;
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class BigInteger_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 数字太大,需要使用 BigInteger 类
// long l = 233333333333333333333333333333L;
BigInteger bigInteger = new BigInteger("23333333333333333333333333");
BigInteger bigInteger1 = new BigInteger("1000000");
System.out.println(bigInteger);
// 加减乘除使用对应方法
System.out.println(bigInteger.add(bigInteger1));
System.out.println(bigInteger.subtract(bigInteger1));
System.out.println(bigInteger.divide(bigInteger1));
System.out.println(bigInteger.multiply(bigInteger1));
}
}package com.bbedu.bignum;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.math.RoundingMode;
public class BigDecimal_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double d = 1111.1111111111119999999999999999;
System.out.println(d);
// 需要保存精度很高的数时,使用 BigDecimal
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal("1111.1111111111119999999999999999");
System.out.println(bigDecimal);
// 加减乘除需要使用特定方法
BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal("100.9999999999");
System.out.println(bigDecimal.add(bigDecimal1));
System.out.println(bigDecimal.subtract(bigDecimal1));
System.out.println(bigDecimal.divide(bigDecimal1, RoundingMode.CEILING)); //可能异常:ArithmeticException: Non-terminating decimal
System.out.println(bigDecimal.multiply(bigDecimal1));
}
}日期类

package com.bbedu.date_;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class Date01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
// 过去当前系统时间,通常需要格式转换
Date d1 = new Date();
System.out.println(d1);
System.out.println(d1.getTime());
Date date = new Date(92345678);
System.out.println(date);
// 参见手册
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 hh:mm:ss E");
String format = simpleDateFormat.format(d1);
System.out.println(format);
// 字符串转 Date
String s = "2022年10月13日 02:33:02 周四";
Date parse = simpleDateFormat.parse(s);
System.out.println(parse);
}
}
package com.bbedu.date_;
import java.util.Calendar;
public class Calendar_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println("c=" + c);
// 需要自己组合:
System.out.println("年:" + c.get(Calendar.YEAR));
System.out.println("月:" + (c.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1)); // 月从0开始
System.out.println("日:" + c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH));
}
}

package com.bbedu.date_;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
public class LocalDate_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 第三代日期
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(now);
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String format = dateTimeFormatter.format(now);
System.out.println(format);
System.out.println("年=" + now.getYear());
System.out.println("月=" + now.getMonthValue());
System.out.println("月=" + now.getMonth());
System.out.println("日=" + now.getDayOfMonth());
System.out.println("时=" + now.getHour());
System.out.println("分=" + now.getMinute());
System.out.println("秒=" + now.getSecond());
LocalDate now1 = LocalDate.now();
LocalTime now2 = LocalTime.now();
System.out.println(now1);
System.out.println(now2);
}
}
package com.bbedu.date_;
import java.util.Date;
import java.time.Instant;
public class Instant_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Instant now = Instant.now();
System.out.println(now);
// from 方法 将 Instant 转为 Date 对象
Date date = Date.from(now);
System.out.println(date);
// toInstant 方法将 Date 转为 Instant
Instant instant = date.toInstant();
System.out.println(instant);
}
}
使用时查看 API 即可
本章作业

package com.bbedu.homework;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Homework01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcdef";
System.out.println(reverse(str, 2, 4));
}
public static String reverse(String str, int start, int end){
if(! (str != null && start >= 0 && end > start && end < str.length())){
throw new RuntimeException("参数不正确");
}
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
char temp = ' ';
while (start < end){
temp = chars[start];
chars[start] = chars[end];
chars[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
return Arrays.toString(chars);
}
}
package com.bbedu.homework;
public class Homework02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "Tom";
String pwd = "123456";
String email = "tom@qq.com";
try {
userRegister(name, pwd, email);
System.out.println("注册成功");
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
public static void userRegister(String name, String pwd, String email){
int nameLength = name.length();
if(!(nameLength >= 2 && nameLength <= 4)){
throw new RuntimeException("用户名长度在[2, 4]");
}
if(!(pwd.length() == 6 && isDigital(pwd))){
throw new RuntimeException("密码长度为6,且全部为数字");
}
int i = email.indexOf('@');
int j = email.indexOf('.');
if(!( i > 0 && j > i)){
throw new RuntimeException("邮箱有误");
}
}
public static boolean isDigital(String str){
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
if(chars[i] < '0' || chars[i] > '9'){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
package com.bbedu.homework;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Homework03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(nameFormat("Chen xue Bin"));
System.out.println(nameFormat("William jefferson Clinton"));
}
public static String nameFormat(String name){
if(name == null){
System.out.println("不能为空");
return null;
}
String[] s = name.split(" ");
if(s.length != 3){
System.out.println("输入格式不正确");
return null;
}
// StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
// stringBuffer.append(s[0]);
// stringBuffer.append(",");
// stringBuffer.append(s[2]);
// stringBuffer.append(" .");
// stringBuffer.append(s[1].toUpperCase().charAt(0));
// return stringBuffer.toString();
String format = String.format("%s,%s .%c", s[2], s[0], s[1].toUpperCase().charAt(0));
return format;
}
}


评论